Botulinum neurotoxin blocks exocytosis of ach at the neuromuscular junction, setting the stage for this enthralling narrative. This fascinating molecule has captivated the attention of scientists and clinicians alike, revealing its intricate mechanisms of action and therapeutic potential. Delve into the depths of this neurotoxin’s molecular mechanisms, clinical implications, and future research directions.
Botulinum neurotoxin, a potent neurotoxin, exerts its influence at the neuromuscular junction, where it disrupts the delicate balance of neurotransmission. By inhibiting the release of acetylcholine, this toxin weakens and paralyzes muscles, leading to a range of clinical manifestations.
1. Introduction: Botulinum Neurotoxin Blocks Exocytosis Of Ach At The Neuromuscular Junction
Botulinum neurotoxin, a potent neurotoxin produced by Clostridium botulinum, has significant implications in neurophysiology and medicine. The neuromuscular junction (NMJ) is a specialized synapse that facilitates communication between motor neurons and muscle fibers. Botulinum neurotoxin exerts its effects by specifically targeting the NMJ, leading to the inhibition of acetylcholine (ACh) release and subsequent muscle weakness and paralysis.
2. Molecular Mechanisms of Botulinum Neurotoxin
Botulinum neurotoxin is a large protein with a complex structure and function. It consists of a heavy chain responsible for binding to specific receptors on the presynaptic membrane and a light chain that enters the neuron and inhibits neurotransmitter release.
Different serotypes of botulinum neurotoxin exist, each with its unique target and potency.
3. Effects of Botulinum Neurotoxin on Neuromuscular Function
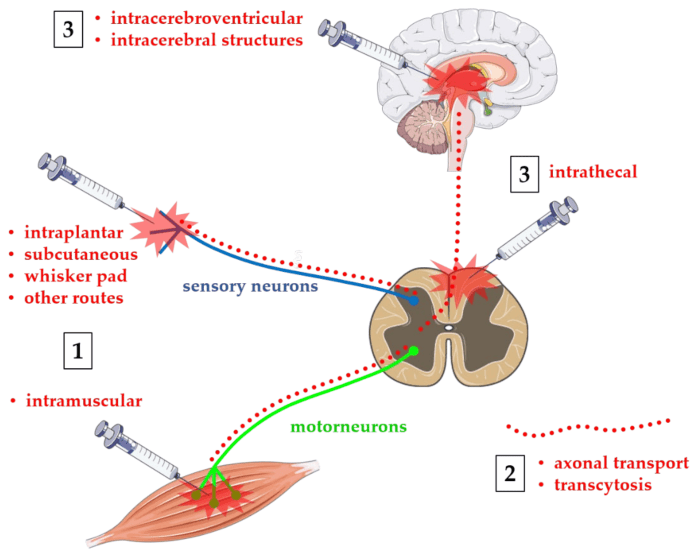
Botulinum neurotoxin impairs neuromuscular transmission by inhibiting ACh release. This results in muscle weakness and paralysis, which can manifest clinically as botulism. Botulism symptoms include muscle weakness, drooping eyelids, difficulty swallowing, and respiratory problems.
4. Therapeutic Applications of Botulinum Neurotoxin
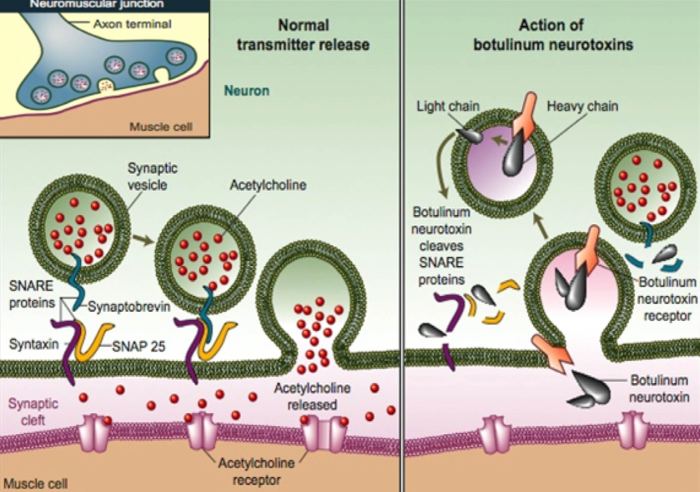
Botulinum neurotoxin has found therapeutic applications in various medical conditions. It is used to treat muscle spasms, dystonia, and other neurological disorders. By selectively targeting and weakening specific muscle groups, botulinum neurotoxin can alleviate symptoms and improve function.
5. Safety and Considerations for Botulinum Neurotoxin Use
Botulinum neurotoxin is generally safe when used appropriately. However, potential adverse effects include muscle weakness, pain at the injection site, and rarely, systemic effects such as respiratory depression. Proper administration, dosage, and patient selection are crucial to minimize risks.
6. Future Directions and Research
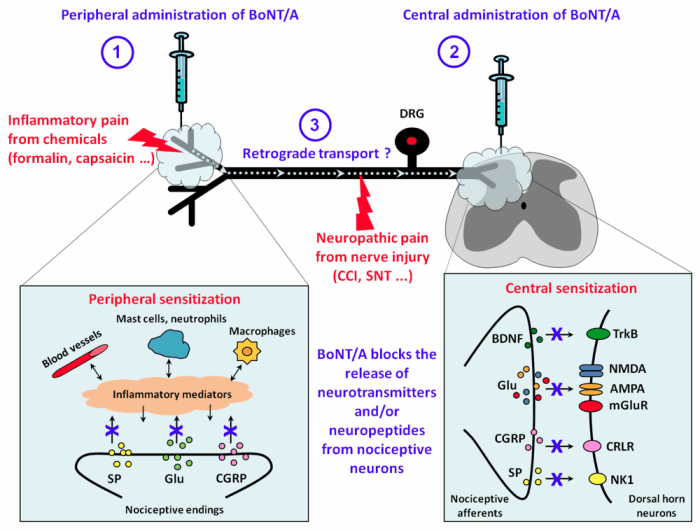
Ongoing research focuses on understanding the mechanisms of action of botulinum neurotoxin and exploring novel therapeutic applications. Advancements in molecular biology and biotechnology may lead to the development of safer and more effective botulinum neurotoxin-based therapies.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the mechanism of action of botulinum neurotoxin?
Botulinum neurotoxin inhibits the release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction, leading to muscle weakness and paralysis.
What are the clinical manifestations of botulism?
Symptoms of botulism include muscle weakness, difficulty swallowing, blurred vision, and respiratory failure.
What are the therapeutic applications of botulinum neurotoxin?
Botulinum neurotoxin is used to treat muscle spasms, dystonia, and other neurological disorders.